For the researchers at ucla s jules stein eye institute who launched the first ever study to show that human embryonic stem cells may help reverse patients disease the history making day began at 4 30 a m.
Success rate of embryonic stem cell treatment.
Humans and animals.
It was an early morning wake up call to be sure but a necessary one to prepare for the groundbreaking work that lay ahead.
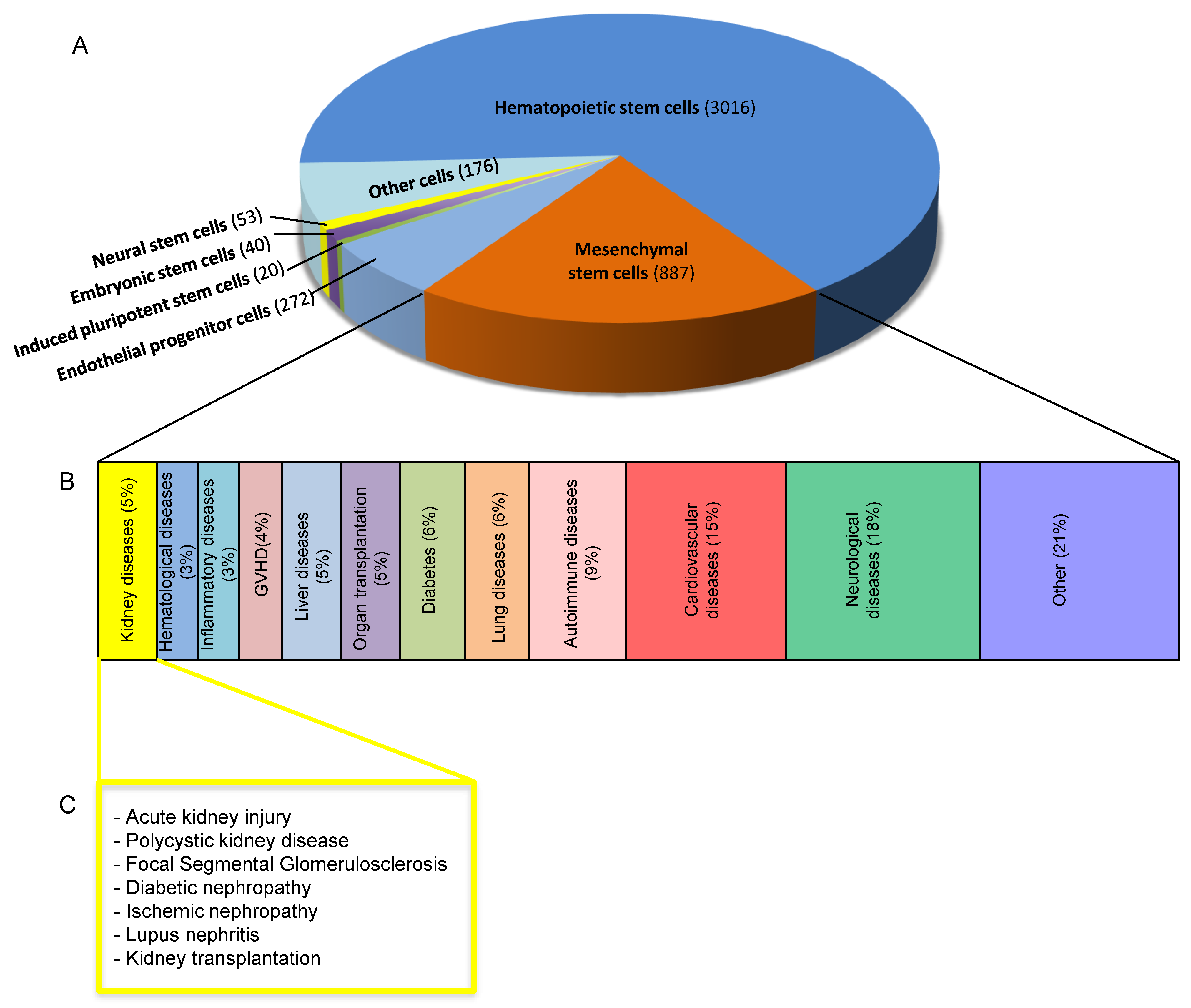
Although official embryonic stem cell treatments have not been created yet more than 6 000 people and 66 different diseases have been treated successfully with cord blood therapies.
For children with immunodeficiency diseases who have been treated in such a way success rates are approaching 90.
But unproven stem cell treatments can be unsafe so get all of the facts.
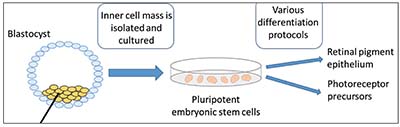
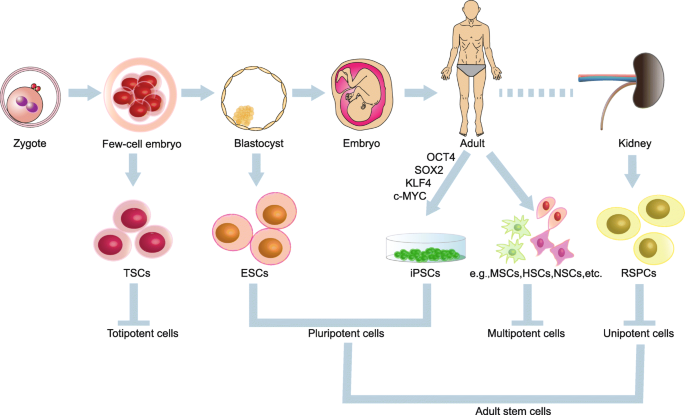
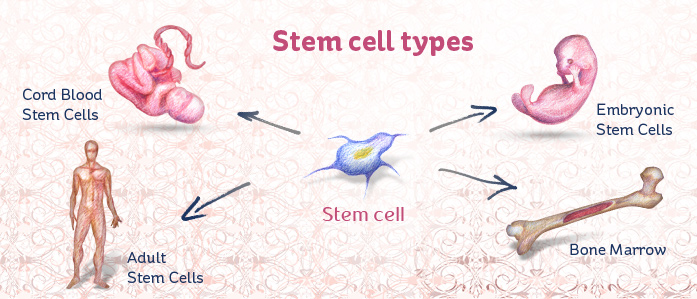
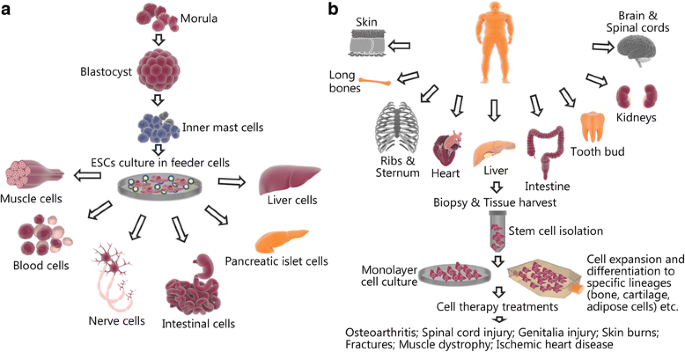
Embryonic stem cells can be obtained from the blastocyst a very early stage of development that consists of a mostly hollow ball of approximately 150 200 cells and is barely visible to the naked eye.
Stem cells can be retrieved and used in treatments while doing no harm to donor or recipient.
A single stem cell treatment will not work on a multitude of unrelated diseases or conditions.
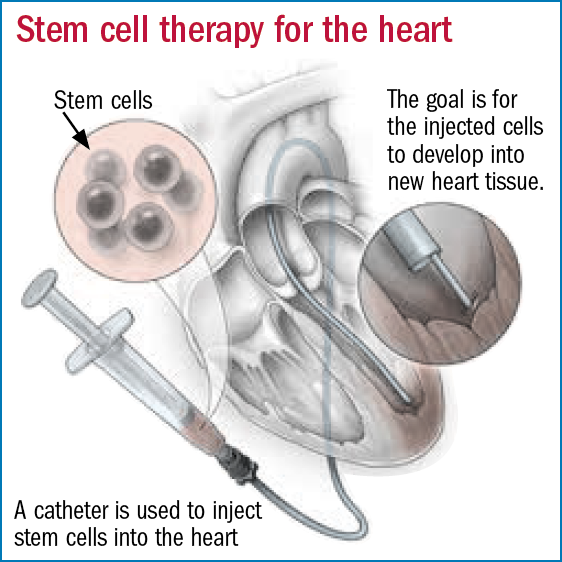
Researchers hope stem cells will one day be effective in the treatment of many medical conditions and diseases.
Yet the success rate of embryonic stem cell research remains a steady zero.
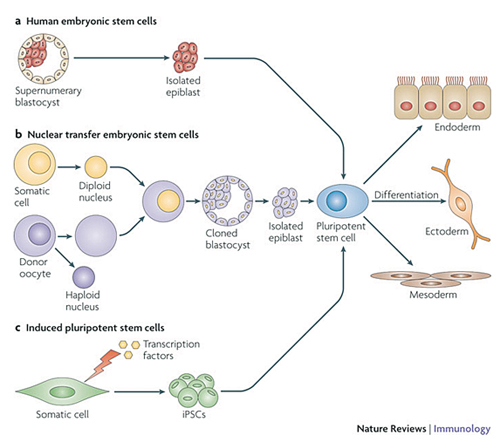
Embryonic stem cells are derived from a blastocyst a type of cell.
Embryonic stem cell research posed a.
Study of 38 000 blood stem cell transplant recipients shows that survival rates increased significantly over 12 years and numbers of patients receiving transplants grew dramatically.
Success rate in use of adult stem cells staggering.