Researchers from kyoto university in japan started a clinical trial this month to treat parkinson s disease with reprogrammed stem cells.
Stem cell treatment for parkinson s disease 2018.
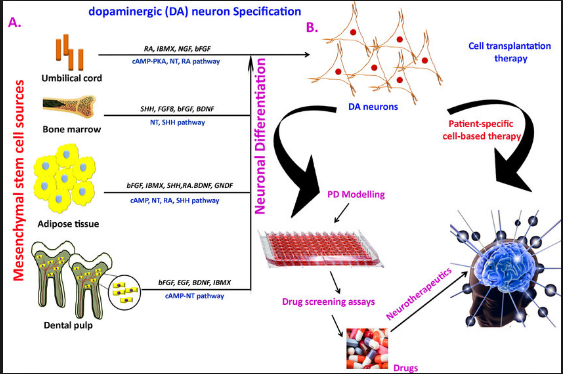
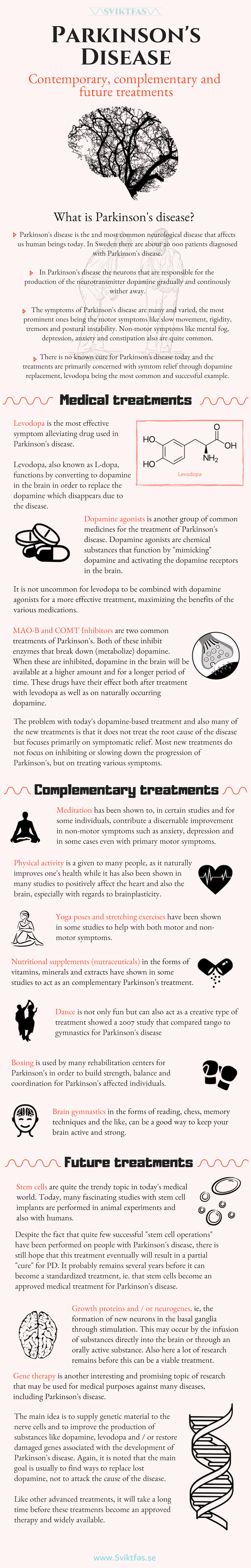
Pluripotent stem cell based therapy for parkinson s disease.
Sonntag a b c bin song a d nayeon lee a d jin hyuk jung a d young cha a d pierre leblanc a d carolyn neff e sek won kong f g bob s.
Current status and future prospects author links open overlay panel kai c.
May 13 2020 at 5 00 p m.
Parkinson s patient improving after first ever stem cell therapy.
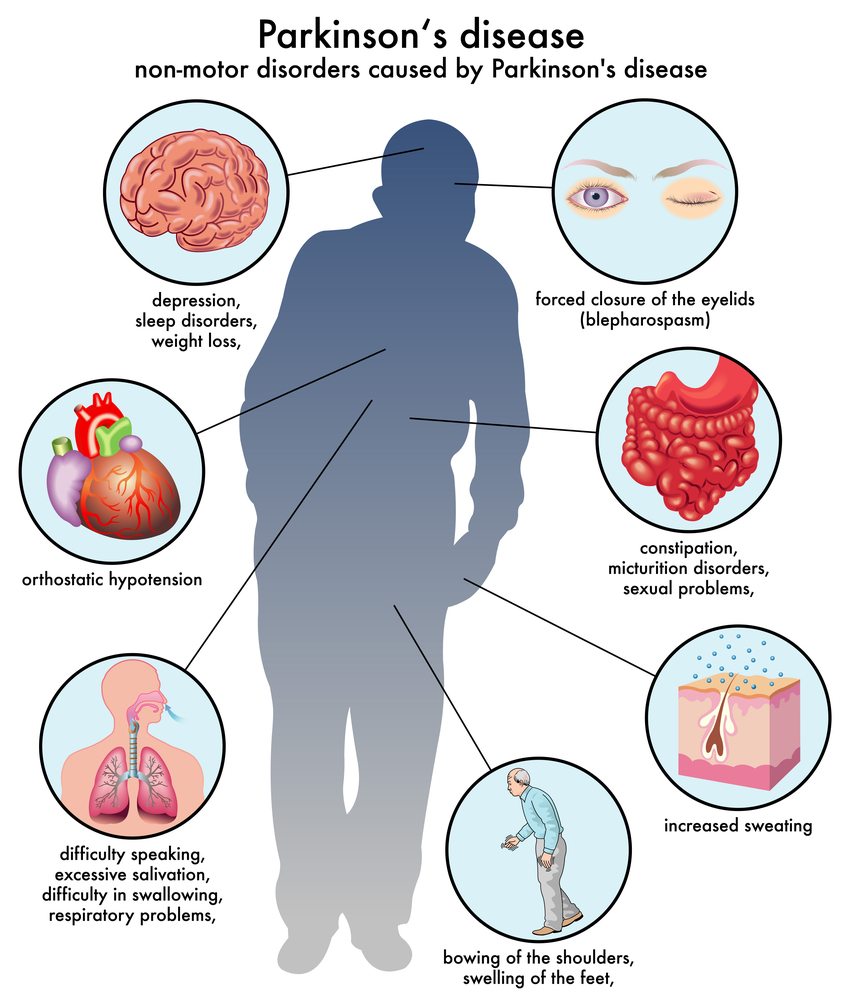
Parkinson s treatments understanding stem cell therapy in parkinson s disease treatment on april 29 2018 the washington post published an article examining commercial stem cell clinics in the united states that market non fda approved treatments directly to the public for a variety of health issues including arthritis macular degeneration and of particular note to us parkinson s disease pd.
Breakthrough in stem cell treatment for parkinson s in a major breakthrough for the treatment of parkinson s disease researchers working with laboratory rats show it is possible to make dopamine cells from embryonic stem cells and transplant them into the brain replacing the cells lost to the disease.
Stem cell treatment for parkison s disease as an option is being intensively researched however when stem cell treatment is used for parkinson s patients can obtain remarkable respite from the condition.
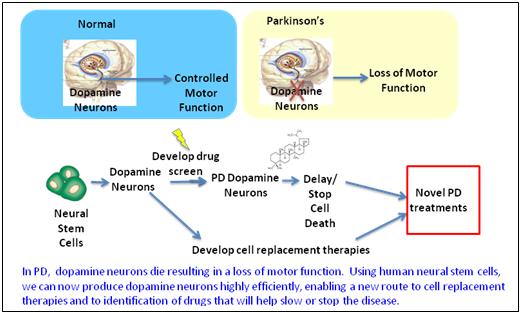
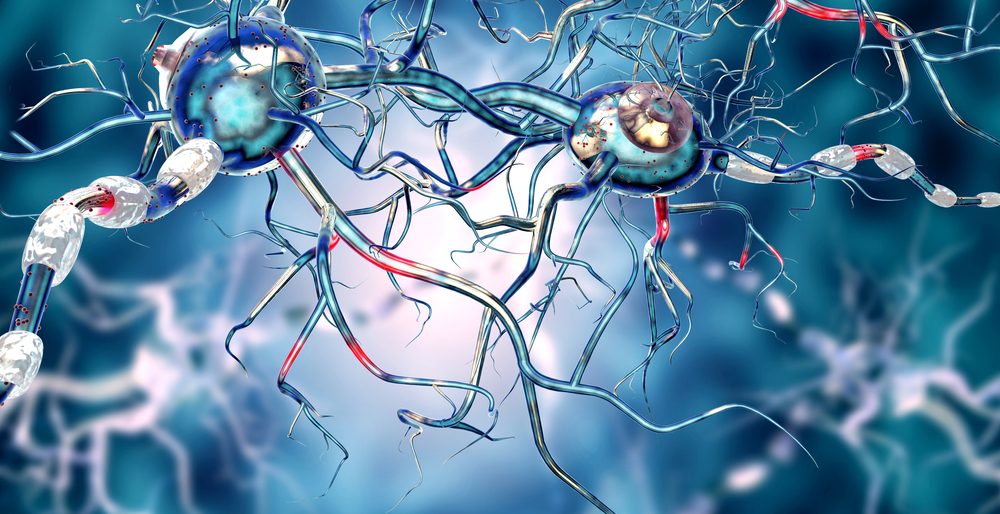
There are no disease modifying treatments and current management is centered on symptom control using predominantly dopaminergic drugs.
Pluripotent stem cell based therapy for parkinson s disease.
This follows the successful restoration of brain cell function in monkeys using these stem cells reported last year.
Now available to patients worldwide fetal stem cell fsc therapy can effectively relieve the symptoms of parkinson s disease.
Carter h jeffrey schweitzer h kwang soo kim a d.
The research in this special issue reflects the responsible advancement of cell therapy for pd.
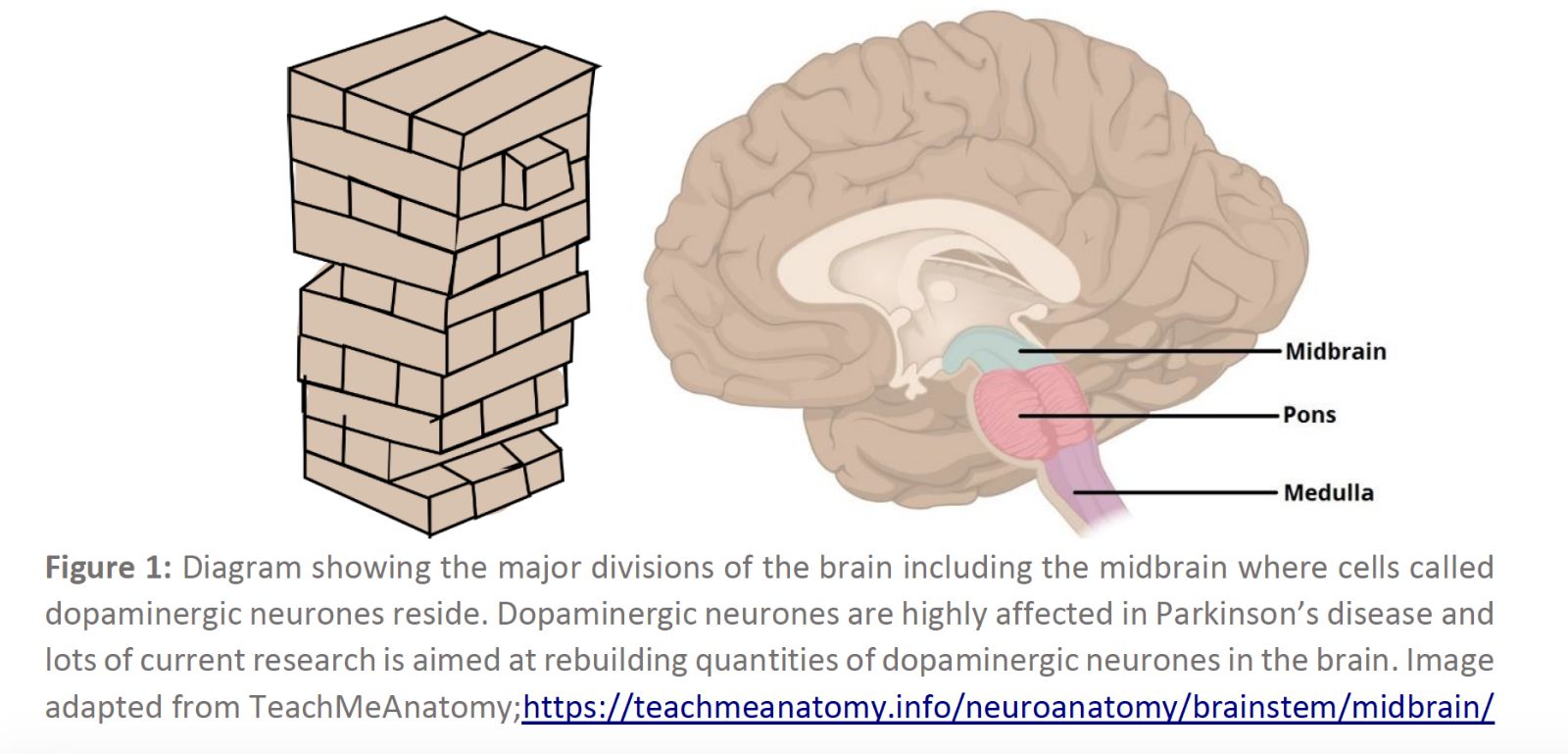
Crucially the stem cells easily turned into the midbrain dopamine neurons that kim and now lopez hoped would treat parkinson s disease.
Kim knew it would take tens of millions of dopamine.
While effective at improving the motor symptoms of pd these treatments result in significant adverse effects due to non targeted and non physiological delivery of dopamine to the brain.
Parker phd editor in chief of the journal said in a press release.